Where Cyber and Biological Worlds Meet: How to Create the Ultimate Financial Control System
Central banks now seek direct control over individuals’ ability to transact. Will the new all-digital system be secured by a biologically-based blockchain, rolled out after a giant cyber false flag?
Going Direct
Central Bank Digital Currencies
The so-called “Covid-19 pandemic” provided cover for initiating what Titus (2021) labels the “Going Direct Reset,” i.e. abolishing the split-circuit system that keeps central bank reserves and retail money separate (as is necessary for a democratic system of “no taxation without representation”) and instead establishing a direct connection between central banks and individuals’ private accounts.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) are a key element of the “Going Direct Reset.” As the head of the Bank for International Settlements, Augustín Carstens, candidly revealed in November 2020, CBDCs mean that “the central bank will have absolute control on the rules and regulations that will determine the use of that expression of central bank liability, and also we will have the technology to enforce that” (Solari, n.d.). In other words, money will no longer exist as a free medium of exchange; instead, there will be a totalitarian control system in which the central bank determines how, when, where, and if one’s tokens can be spent. “Undesirable” attitudes and behaviors will presumably be met with limitations on individuals’ financial transaction freedom (cf. Fitts & Betts, 2023b).
We already know from the Canadian government’s response to the Freedom Convoy in early 2022 that governments are looking to leverage the financial system to quash dissent. In that particular case, some of the truckers and their crowdfunding supporters had their bank accounts frozen and their credit cards cancelled. It is to be expected that financial censorship will be more severe if the central bank can attach conditions to how tokens are and are not used.
The danger of an all-digital financial system, Fitts (2022) explains, is that it can be “converted to an overt slavery system literally overnight.” Yet, as with the entire war for technocracy, the drive for total control is at once a gigantic act of desperation: “Central banks are pushing for central control – they believe if they do not do so, they will lose control” (Fitts & Betts, 2023a; cf. Hughes, 2024a, pp. 358-361). Moreover, given that central banks “do not provide essential functions and their exercise of control is exceptionally damaging and expensive,” the public would be better off without them, both financially and in terms of liberty.
Manufactured Inflation
BlackRock (2019) knew before “Covid-19” that, “in the long run, the growth of money supply drives inflation.” So it proved:
Source: https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/M2SL#0
The historically unprecedented increase of the M1 money supply from under $4,000 billion in 2019 to over $20,000 billion by the start of 2022 indicates a five-fold increase in just over two years. The M2 money supply shows an approximate 50% increase from under $15 billion to almost $22 billion during the same period. The corresponding increase in inflation occurred around a year later.
According to the Federal Reserve (n.d.), M1 = “the sum of currency held by the public and transaction deposits [...] at depository institutions,” such as commercial banks, savings banks, and credit unions. Therefore, the dramatic spike in M1 would not have been possible without Blackrock’s (2019, p. 2) “Going Direct” plan to “to get central bank money directly in the hands of public and private sector spenders” by breaking the traditional split circuit arrangement and injecting massive amounts of money into the retail circuit.
The inevitable high inflation caused by the coordinated actions of central banks around the world created a “cost-of-living crisis” that was then disingenuously blamed on “Putin” and the war in Ukraine that escalated in February 2022, even though the surge in UK inflation from 2 to 10% in a single year began in July 2021 (Rate Inflation, n.d.). UK food prices were 30% higher in October 2023 than in October 2021 (Office for National Statistics, 2023).
We may be looking here at economic warfare against Western populations following a period of shock, known from the CIA playbook: in the 1970s, for instance, “Not only were Chileans in a state of shock following Pinochet’s violent coup, but the country was also traumatized by severe hyperinflation” (Klein, 2007, p. 7). This, in turn, was exploited by Milton Friedman to institute the original economic shock therapy, involving mass privatization of public goods and services in the “most extreme capitalist makeover ever attempted anywhere.”
The roots of such tactics in fact go back much further, e.g. to the Weimar Republic, when the privately owned Reichsbank, effectively taken under J.P. Morgan control under the pretext of reparations, immediately began a campaign of hyperinflation which “essentially destroyed the middle class” (Werner, 2024). That same middle class then placed its faith in Hitler, who betrayed them again through policies that left small businesses to collapse while promoting the major industrial interests (Hughes, 2024b, p. 19).
Thus, although inflation rates have gradually fallen since the end of 2022, we must remain on guard for subsequent inflationary surges as the Omniwar intensifies.
The BIS “Blueprint for the Future Monetary System”
In its “Blueprint for the future monetary system,” the BIS (2023, p. 94) proposes a “unified ledger” model in which “central bank digital currencies, private tokenised monies and other tokenised assets coexist on the same programmable platform.” Thus, the split circuit system is no more: notwithstanding references to “wholesale CBDCs” and “retail CBDCs” (p. 90), there is a “singleness of money” (p. 109).
In a tacit nod to evil, the BIS (2023, p. 94) seeks to assure readers that the unified ledger concept “does not mean ‘one ledger to rule them all’ – a sole ledger that overshadows all other systems in the economy”; rather, multiple ledgers, tailored to the needs of individual jurisdictions, could coexist within it. Nevertheless, the framework for a single global digital currency system is established. In fact, on the same day that the BIS blueprint was published (June 20, 2023), IMF head Kristalina Georgieva stated that her organization was “working hard on the concept of a global CBDC platform” (IMF, 2023, 08:35).
Crypto, according to the BIS (2023, p. 86), “lacks the anchor of the trust in money provided by the central bank” – a staggering claim, given that privately owned central banks have been at the heart of capitalist exploitation and oppression since the early 20th century. The BIS itself should have been liquidated for its role in Nazi money laundering (Hughes, 2024b, pp. 66-67).
Tokens, which are “not merely digital entries in a database,” can be “customised to meet specific user or regulatory requirements that apply to individual assets” (BIS, 2023, p. 88), i.e., “money” becomes programmable and conditions can be attached to its usage.
The Bank for International Settlements’ “Unified Ledger” Model
Merging Human Bodies and the Financial System
Towards a Biologically-based Blockchain?
The diabolical Microsoft patent WO/2020/060606, granted in April 2020, proposes to “award cryptocurrency to the user whose body activity data is verified” by any “sensor or scanner that can measure or sense body activity or scan [the] human body.” Here, human bodies merge with the financial system. In place of the massive computation work required by conventional cryptocurrency systems, the patent states, “data generated based on the body activity of the user can be a proof-of-work, and therefore, a user can solve the computationally difficult problem unconsciously.” In other words, human bodies can be used to mine crypto, in which case the blockchain can be based on human biology. Although crypto typically relies on a decentralized blockchain, the patent points out that “blockchain-based cryptocurrency can also be implemented in a centralized system having a central point of control over the cryptocurrency.” So, in principle, a CBDC could allow the central bank to have control over a biologically-based blockchain whose security is premised on the unique bodily data (e.g. DNA) of its users.
Lest the idea of a biologically based blockchain sound like science fiction, consider the following passage, published in an IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) journal:
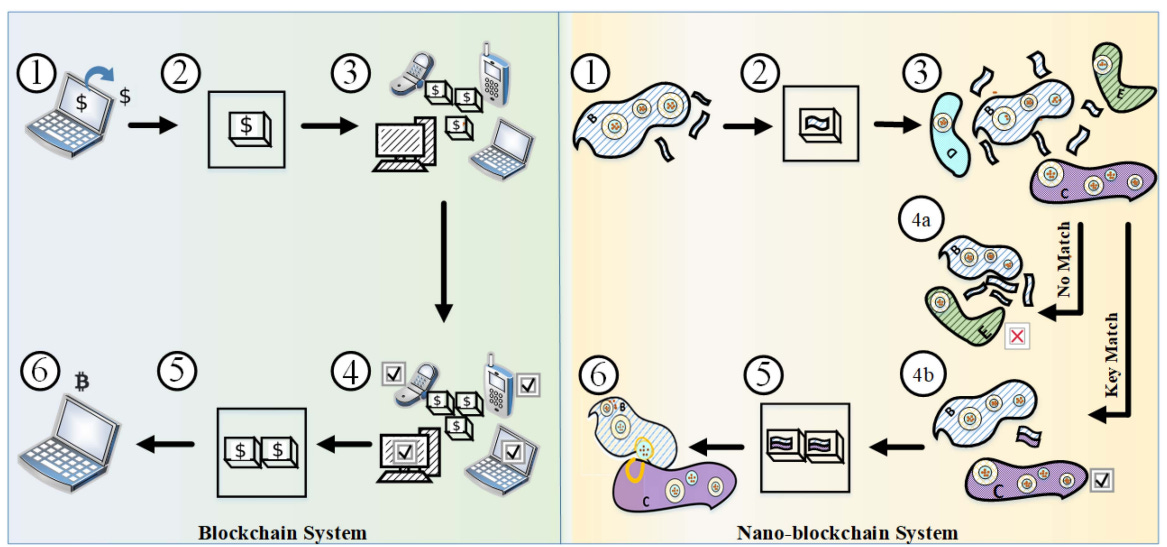
We envisage a new research direction and coin the term – “BioBlock” – a blockchain-inspired nanonetworking security mechanism since the existing macro-scale security solutions are not suitable for nanoscale. Specifically, we propose a biological ledger-based relay model to secure targeted drug delivery without affecting surrounding healthy tissues. In BioBlock, each successful transaction generates a block with genetic signatures of the bionodes in the nanonetwork, which eventually gets validated by the neighboring bionodes. (Misra et al., 2023, my emphasis)
Misra et al. (2023), Fig. 2. Graphical comparison between Blockchain and BioBlock functionalities.
Thus, it is theoretically possible to construct a blockchain at the nano level, based on genetic signatures. Groninger’s (2022) prediction that, “ultimately, blockchain and DNA will merge” appears plausible in this context.
Could a “BioBlock”-style intracorporeal nanonetwork communicate securely with other networks? Almost certainly. Israeli scientist Ido Bachelet, for instance, received a 2013-2017 European Commission grant to work on “DNA nano-routers” (Cordis, n.d.) and collaborated with Pfizer on a project involving a network of DNA nanobots with miniature antennae capable of responding to external signals (Weinreb, 2015).
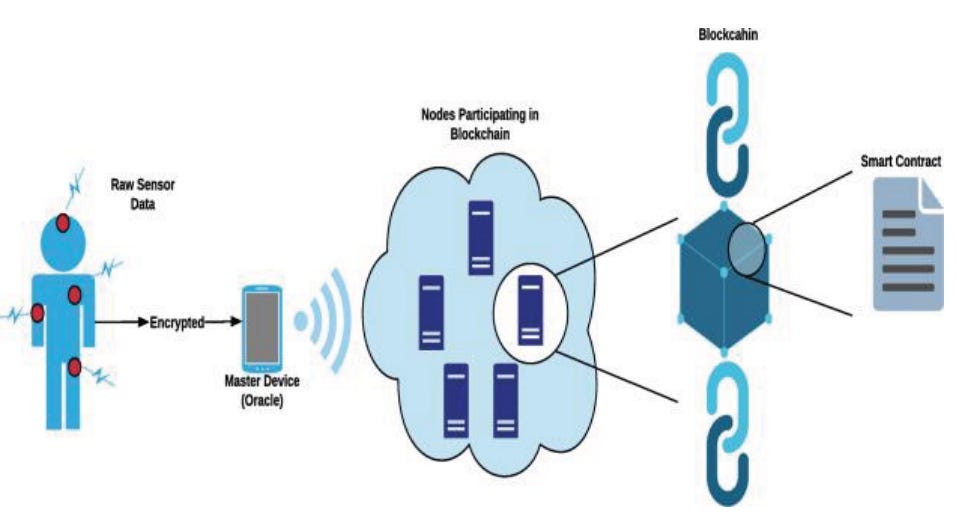
According to a 2019 IEEE article, it is possible to integrate blockchain technology with a wireless body area network:
Source: Kumari et al. (2019)
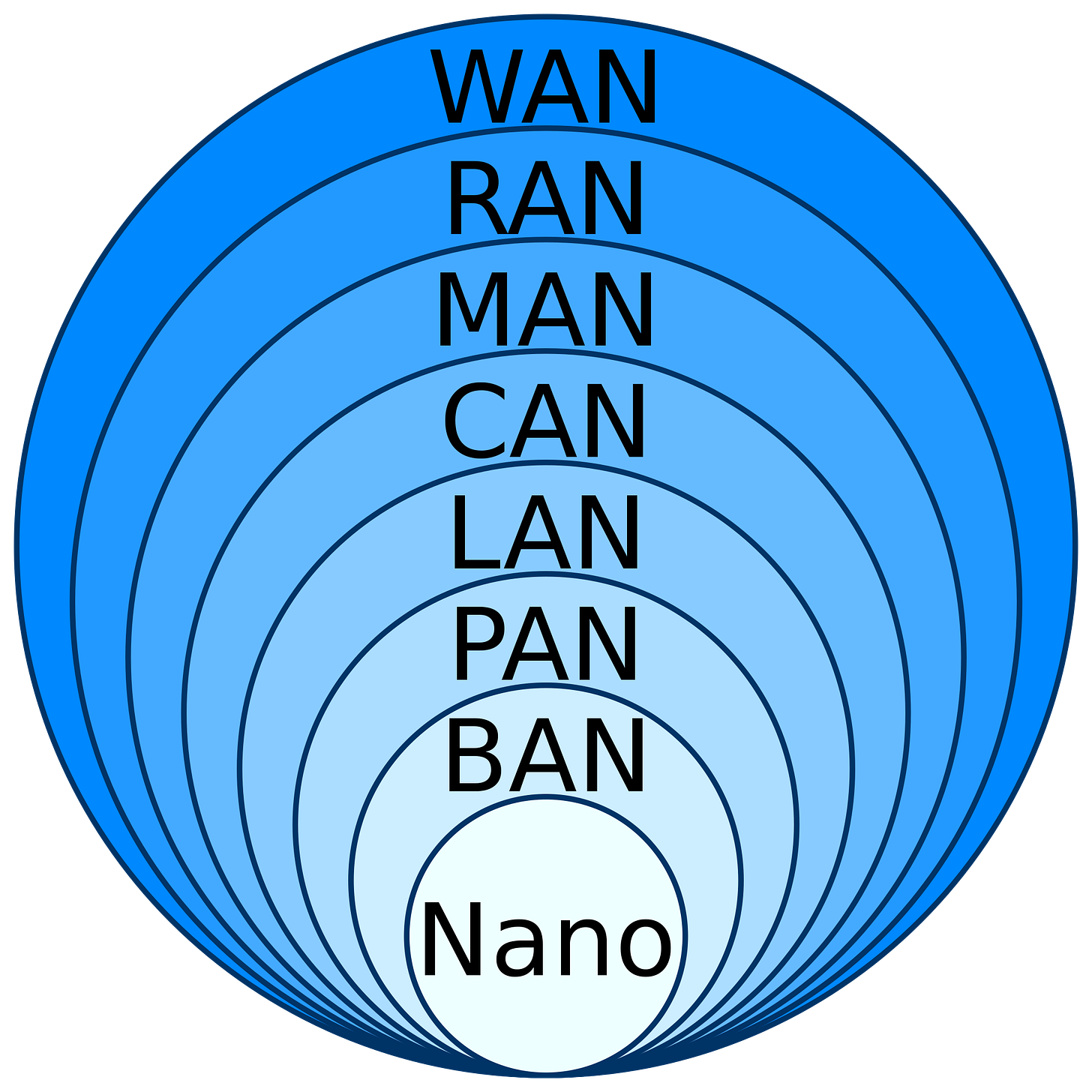
So, in principle, it is possible to build blockchain secure networks at every level, from the nano level, through the Body Area Network, up to the Personal, Local, Campus, Metropolitan, Radio, and Wide area networks:
Source: https://networklessons.com/cisco/evolving-technologies/iot-standards-and-protocols
The end result would be an unhackable “network of networks,” allowing the technocratic control grid to reach right down into the level of human DNA.
Sabrina Wallace, who claims to be the daughter of two Black Project scientists and to have been experimented upon as a child at the Menninger Foundation, claims that the DoD’s autonomous weapons program, involving MQ-9 Reaper drones, is “tethered to your DNA” (cited in Bruce, 2024). Although there is no way of verifying this claim, it, too, is consistent with the idea of DNA being used as a unique identifier of human bodies connected to a control network. Troublingly, it also highlights the potential military application of such technologies.
We should heed the estimate by Harvard historian of science, Peter Galison (2004, p. 231), that classified scientific research is “on the order of five to ten times larger than the open literature that finds its way to our libraries.” We should also note the claim of NASA Langley’s Dennis Bushnell (2001, p. 5) that much military-funded R&D remains in inventory for over 40 years. The point is that the public has no idea of what has long been technologically possible behind the scenes. For example, although a “biological ledger-based relay model” (Misra et al., 2023) has only recently slid into public view as a theoretical possibility, the military may have developed such technology years ago. In the context of the Omniwar, the advantages conferred by classified technology are that it can be deployed by stealth and that the public would not believe it to be real even if presented with the evidence (cf. Wood, 2011).
“Vaccines” to “Plug and Play” in the New Biosecure Economy?
In 2021, IMF chief Kristalina Georgieva made an extraordinary pronouncement: “This year, next year, vaccine policy is economic policy, and it is an even higher priority than the traditional tools of fiscal and monetary policy. Why? Because without it, we cannot turn the fate of the world economy around” (cited in Australian Voice, 2021). What did she mean by this? How could “vaccines” be more important than fiscal and monetary policy in rescuing the global economy?
A clue, perhaps, is to be found in Georgieva’s (2020) previous proclamation of a “new Bretton Woods moment,” referring to the 1944 conference which laid down the basis for the post-1945 international monetary and financial system. Evidently, and consistent with the war for technocracy, the ambition now is to overhaul the entire monetary and financial system.
Reading between the lines of Georgieva’s two speeches, it seems that “vaccines,” for whatever reason, are indispensable to the replacement system. On the same day that Georgieva gave her “new Bretton Woods” speech (October 15, 2020), YouTube released its policy on “managing harmful conspiracy theories,” to make sure none of its users were allowed to question the coming “vaccine” rollout.
Consistent with transhumanism and the maturing biosecurity state, the aim seems to be to make human bodies part of a revolutionized global financial system, possibly involving a biologically-based “unified ledger.” Critics have already observed, with respect to so-called “vaccine passports,” that, “like a peripheral device we ‘plug and play’ into the smartphone, the hypodermic needle becomes the plug that will enable us to ‘play’ in the new biosecure economy [...]” (Broudy, 2021, p. 108).
But could the “plug and play” metaphor be apt in another, more literal way? Could it be that “mRNA vaccines,” which do not meet the traditional definition of a vaccine (Hughes, 2022a, pp. 210-211) and could be providing cover for military technologies (Hughes, 2024a, pp. 342-345), are in fact intended as a delivery system for technologies that are capable of connecting human bodies to EMF networks? Johnson et al. (2024), drawing on two decades of military intelligence literature, present a large amount of circumstantial and empirical evidence that this could well be the case, although there is, as yet, no scientific proof.
A comprehensive scientific investigation of “vaccine” contents for potential nanotechnology requires access to prohibitively expensive equipment such as precision Atomic Force Microscopes and Scanning Tunnelling Microscopes, which, used in conjunction with Electron Microscopes, are capable of precisely characterizing nanoparticles and nanomaterials, including those involving DNA. However, the cost of such investigations, which can run into millions of dollars, ensures that they are monopolized by institutions that have been comprehensively cleansed of independent and critical activities, particularly since the “mis-,” “dis-,” and “mal-” information purges of the Covid era.
The “MAC Address” Phenomenon
The jury remains out on claims that “Covid-19 vaccine” and swab recipients emit Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Media Access Control (MAC) addresses, which would be evidence of connection to an external network. Skeptics claim that the observed “dynamic or randomized MAC addresses are most likely offered by nearby devices as handshakes or feelers” (Tannahill, 2022). On the other hand, there are very good reasons why the “MAC address” phenomenon should not be too readily dismissed, certainly not without proper scientific investigation of the matter (Johnson et al., 2024).
If it could be shown scientifically that dynamic or randomized MAC addresses are being emitted from human bodies, then by implication those bodies have become like Apple platforms, looking to “find and connect to a known Wi-Fi network or to assist Location Services for apps that use geofences” while keeping the device private by changing the randomized address for each new network joined (Apple, n.d.). In this way, the bodies would be securely connected to the network.
Frustratingly, although it should be straightforward, in principle, to design a robust experiment to test the “MAC address” hypothesis – which is potentially of pivotal importance in exposing the worldwide implementation of the “IT/Bio/Nano” warfare paradigm forecast for the 2020s (Bushnell, 2001, p. 13) – scientists are not doing the work. This is something which needs to change.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity and the Financial System
As Celik & Eltawil (2022) observe, “as the cyber and biological worlds meet, security risks and privacy concerns take center stage.” Hacking a website or a server is one thing; hacking a human body is quite another. The replacement financial system must be 100% secure. As we have seen, the ultimate secure blockchain could be tethered to human DNA. But before bringing in the new system, faith in existing security protocols must be destroyed,
In November 2019, the Carnegie FinCyber project (n.d.), which was launched in 2015, announced its intention to produce an “International Strategy for Cybersecurity and the Global Financial System 2021-2024.” The resultant report, published in November 2020, drew on an advisory group including representatives from the Bank of England, the Federal Reserve, HSBC, SWIFT, Amazon, Accenture, the IMF, the WEF, the Munich Security Conference, and CrowdStrike, among others (Maurer & Nelson, 2020, Appendix F). It claims that the boundary between financial services firms and tech companies is blurring and cites the Financial Stability Board’s warning in April 2020 that “cyber incidents pose a threat to the stability of the global financial system” (Maurer & Nelson, 2020, pp. 1-2). “One thing is clear,” the report claims: “it is not a question of if a major incident will happen, but when” (p. 2).
In July 2020, introducing the first Cyber Polygon exercise (aimed at improving “cyber resilience” worldwide), Klaus Schwab (2020, 01:15) pointed to the threat of a “comprehensive cyber attack [which] could bring a complete halt to the power supply, transportation, hospitals, our society as a whole,” rendering the “Covid-19” crisis but “a small disturbance in comparison.” The World Economic Forum (2012; 2021a; 2021b) has repeatedly underscored the danger of a “cyber pandemic.” Critics have speculated that the Cyber Polygon exercises could serve a similar function to anti-terrorist drills or pandemic preparedness exercises in terms of setting the stage for a future false flag operation (Korinth, 2022).
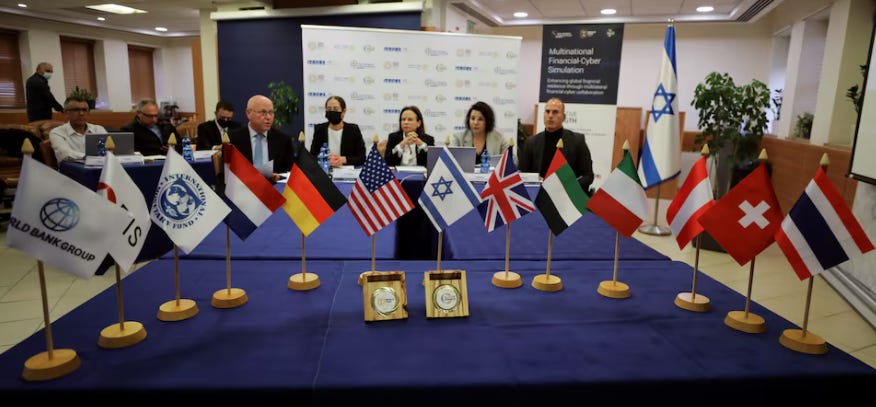
A similar “war game” exercise, as the Israeli Finance Ministry referred to it (Scheer, 2021), took place over ten days in Jerusalem in December 2021. Treasury officials from ten countries, as well as representatives from the IMF, World Bank, and Bank for International Settlements participated in the so-called “Collective Strength” initiative, modelling responses to various hypothetical cyber attacks on the global financial system.
Participants at the “Collective Strength” initiative, Jerusalem, December 2021 (Scheer, 2021)
Media Reports of Cyber Fragility
As though to highlight the fragility of the system, there have been numerous reports of high-profile hacks since 2020. The SolarWinds hack of early 2020, for instance, was reportedly used to gain access to the systems of various U.S. government agencies, Fortune 500 companies, and other large organisations (Jibilian & Canales, 2021). One of the victims was cybersecurity firm FireEye, whose “arsenal of hacking tools used to test the defenses of its clients” was stolen (Bing & Menn, 2020). Underscoring the danger, the National Nuclear Security Administration, which maintains the U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile, was reportedly hacked in December 2020 (Turton et al., 2020).
Cyber attacks in the United States in 2021 reportedly closed down a major oil pipeline (de Lea, 2021), beef plants (Batista, 2021), and 200 companies using Kaseya software (Tidy, 2021). In April 2021, the details of 533 million Facebook users were reportedly stolen and posted online (Holmes, 2021).
The reported attacks have been transnational, e.g. on health IT infrastructure in the UK (Knowles, 2020), Brazil (Reuters, 2021), and Ireland (Sheils McNamee, 2021).
Determining the provenance of the above cyber attacks, assuming they were real (as opposed to merely reported), is close to impossible for any member of the public. But the fact that they followed almost seamlessly from the Carnegie FinCyber announcement of November 2019, coinciding with the Cyber Polygon and Collective Strength exercises, raises the possibility that we are looking here at propaganda – either involving actual cyber attacks (propaganda of the deed), or possibly fake attacks in some cases.
Further adding to the impression that the internet could go awry at any moment, there were unexpected service outages on the major platforms. This scarcely seems conceivable given that those platforms are basically intelligence operations with unlimited funding (Corbett, 2019). Yet, to the shock of users, YouTube, Google, Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Amazon Web Services variously went down at certain points (including November 11, 2020, December 14, 2020, April 8, 2021, October 4, 2021, December 16, 2021). In July 2024, a software update from CrowdStrike (one of the advisors on the Carnegie FinCyber report above) caused Microsoft software around the world to stop functioning (Bishop & Kharpal, 2024).
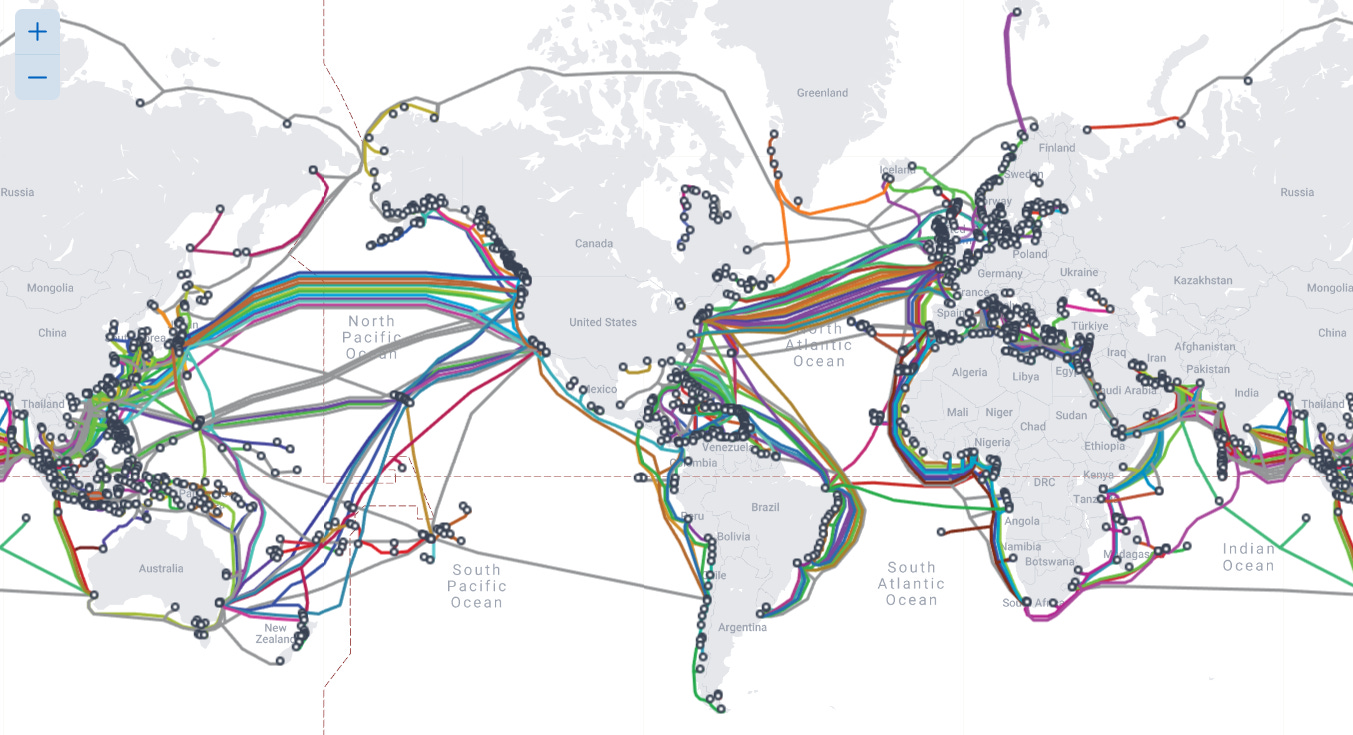
The media has hinted that the undersea cable network that powers the internet could be damaged, e.g., by solar storms (Randall, 2021) or a volcanic eruption, revealing “the extreme vulnerabilities of the infrastructure that underpins the workings of the internet” (Yerushalmy, 2024). We know from Nord Stream that bad actors are prepared to blow up undersea pipelines, and given that there are only 552 submarine communication cables worldwide, mostly concentrated in the North Atlantic and North Pacific (TeleGeometry, n.d.), it would not be difficult for those with the right equipment to cause mayhem.
TeleGeometry’s (n.d.) Submarine Cable Map
Cyber Attacks and the Deep State
The mainstream media routinely attributes cyber attacks, or potential cyber attacks, to the Russian bogeyman (Geller, 2020; Westby, 2020; Harding, 2020; Turton et al. (2020); Jibilian & Canales, 2021; O’Donnell & Jones, 2022; Ruffini, 2022; Foy, 2022; Barton, 2024). Yet, as Webb (2021) points out, Russia’s leading role at Cyber Polygon suggests that the “Russian hacker” narrative is intended only for the Western public.
In reality, the intended cybersecurity measures are not to protect the public from external threats at all. Rather, they are to protect the ruling class from the public by making the technocratic control grid, including its financial component, incorruptible.
The most serious threat of cyber attacks emanates from governments against their own citizens. In Cuba and Kazakhstan, protests were met by the government instituting an internet blackout (Cordoba et al., 2021; Baker, 2022). This shows that the real power to pull the plug on the internet lies, not with sub-state actors, but, rather, with governments and the forces that control them. We know from the case of Anhalt-Bitterfeld in Germany that a paralyzing cyber attack can be invoked to declare a state of emergency (DW, 2021). Thus, a transnationally engineered internet outage could, like “9/11” or “Covid-19,” be used as the pretext for emergency rule, and possibly martial law.
Is there any evidence that planners are thinking along these lines? Quite possibly. Back in October 2012, U.S. Defense Secretary Leon Panetta claimed that the United States was facing a potential “cyber Pearl Harbour” perpetrated by foreign hackers (Brewster, 2012). This echoes the multiple premonitions of a “new Pearl Harbour” that appeared between 1997 and 2001, setting the stage for “9/11” (Hughes, 2020, pp. 76–77). The erstwhile Homeland Security Secretary, Janet Napolitano, warned in 2013 of a “cyber 9/11” (Kerr, 2013). Senator Joseph Lieberman spent years campaigning for an “Internet kill switch that would grant the president vast power of private networks during a ‘national cyber emergency’” (McCullagh, 2012).
In 2023, the U.S. Naval Institute presented a hypothetical scenario in which the Japanese island of Okinawa is hit by an orchestrated internet blackout:
By synchronizing the release of disinformation with the blackout, the attackers capitalized on their targets’ increased susceptibility to misinformation. But the timing also reduced U.S. and Japanese leaders’ maneuver space by denying them opportunities to reinforce their citizens’ cohesion and will. If the vignette had taken the story further, the attack could have escalated to low-level kinetic operations attributed to Okinawa opposition groups, followed by a full-scale “intervention” to restore peace on the island (MacDonald & Ratcliffe, 2023).
Here, one need only replace “Okinawa” with a country/countries of one’s choosing, and a recipe for martial law unfolds: internet blackout, offline misinformation, undermining of democratic leadership, use of agents provocateurs to stoke social chaos/civil war, and use of the Army to restore order.
In the internet blackout scenario, while the people would struggle to communicate, make sense of what was happening, and organize, governments would have no such difficulties, judging by President Obama’s Executive Order of July 2012 titled “Assignment of National Security and Emergency Preparedness Communications Functions.” The EO states that the U.S. Federal Government will “have the ability to communicate at all times and under all circumstances,” both “within itself and with: the legislative and judicial branches; State, local, territorial, and tribal governments; private sector entities; and the public, allies, and other nations” (White House, 2012). So, presumably there is a separate, ultra-secure communications network for the transnational deep state to use, which ordinary citizens do not have access to. This places the deep state at a decisive advantage in its Omniwar against humanity, should it move to temporarily shut off the internet.
Presumably, the internet would only return with military-grade cyber security protocols, allowing for total technocratic control.
Feature Image Credit: Misra et al. (2023), Fig. 2.
Go paid at the $5 a month level, and we will send you both the PDF and e-Pub versions of “Government” - The Biggest Scam in History… Exposed! and a coupon code for 10% off anything in the Government-Scam.com/Store.
Go paid at the $50 a year level, and we will send you a free paperback edition of Etienne’s book “Government” - The Biggest Scam in History… Exposed! OR a 64GB Liberator flash drive if you live in the US. If you are international, we will give you a $10 credit towards shipping if you agree to pay the remainder.
Support us at the $250 Founding Member Level and get a signed high-resolution hardcover of “Government” + Liberator flash drive + Larken Rose’s The Most Dangerous Superstition + Art of Liberty Foundation Stickers delivered anywhere in the world. Our only option for signed copies besides catching Etienne @ an event.